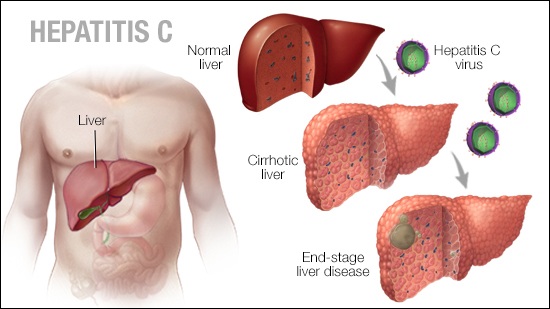
Hepatitis C is a viral and transmittable disease caused by the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). Chronic hepatitis refers to the advanced stages of the ailment if it is left untreated for extended periods.
Symptoms of Chronic Hepatitis C:
Although Hepatitis C shows little to no indications in the initial stages, a few symptoms appear as the disease progresses. Some of them include:
- Continual bleeding
- Yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin
- Red or purple spots on the skin
- Itchy skin and red palms
- Fatigue, nausea, and dizziness
- Loss of appetite
- Dark color of urine
- Light-colored stool
- Fever and weakness
- Easy bruising
- Jaundice
- Abdominal swelling and pain
- Abrupt weight loss
- Confusion, incoherent speech, and headache
Complications due to Chronic Hepatitis C:
Untreated Hepatitis C can lead to a barrage of complications that may even turn lethal for the affected individual. They include:
- High pressure in the blood veins of the liver (portal hypertension)
- Spleen enlargement (splenomegaly)
- Fluid collection in and infection of the stomach (ascites)
- Multi-organ failure
- Liver cancer or failure
- Internal bleeding
- Anemia
- Cirrhosis
- Loss of bone strength and weight
- Type 2 diabetes
- Blood discharge from mouth or rectum
- Disproportionate swelling of the abdomen and legs
- Toxin buildup in the brain (hepatic encephalopathy)
Risk Factors of Chronic Hepatitis C:
It is a fact that Hepatitis C reaches a chronic state if untreated for a long time. Nevertheless, specific factors can make one susceptible to developing the ailment and lead to a worsened condition. A few of them are:
- Excessive intake of alcohol and injection drug use
- An undue and unwarranted buildup of fat in the liver
- Obesity
- Coronary artery diseases
- Liver inflammation
- Steroid treatments
- Excessive buildup of copper and iron in the blood
- Genetic disposition
- Autoimmune disorders
- Continued exposure to radiation
Transmission of Chronic Hepatitis C:
Chronic Hepatitis C can be transmitted from one individual to another through body fluids. Hence, its communication can be through the following methods:
- Blood transfusions
- Organ transplants
- Shared personal items like toothbrush, razer, cutlery, and so on with the affected individual
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Passing of body fluid through kissing, used needles, etc.
- Transmission from mother to child through the placenta
Treatment:
Doctors use a combination of 100 mg of Velpatasvir and 400 mg of Sofosbuvir, called Velakast, for chronic Hepatitis C treatment. It slows down the process of multiplication of the virus and stops it from spreading to other parts of the body.





 +91-9811604444/ 9811604424/ 9999064250
+91-9811604444/ 9811604424/ 9999064250  8(800)100-47-90
8(800)100-47-90








Nice educational post. I love it…